Federalists vs anti federalists worksheet – Dive into the riveting debate between Federalists and Anti-Federalists with our comprehensive worksheet, a journey through the pivotal moments that shaped the United States Constitution. Explore their contrasting beliefs, arguments, and lasting impact on American politics.
Federalists vs Anti-Federalists: Historical Context
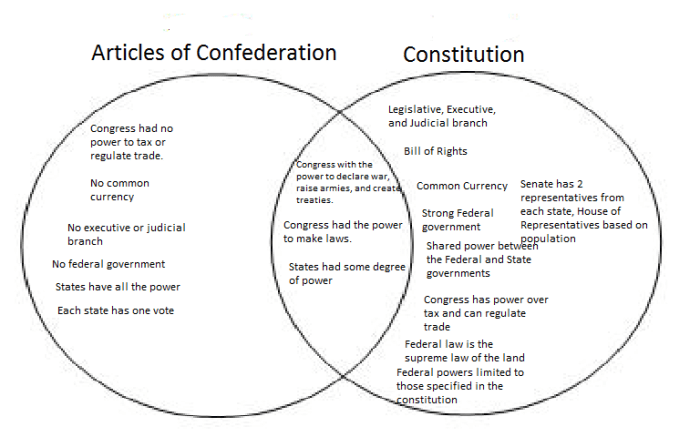
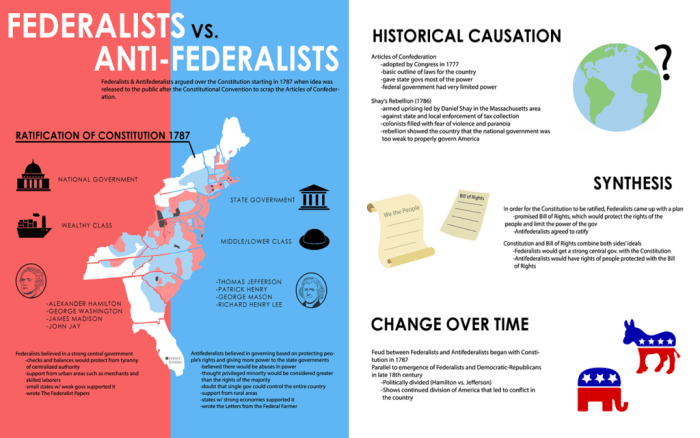
The debate between Federalists and Anti-Federalists emerged amidst the political and historical backdrop of the post-Revolutionary War era in the United States. The Articles of Confederation, the governing document of the newly formed nation, proved inadequate in addressing the challenges of a rapidly growing and diverse country.
In response, a Constitutional Convention was convened in Philadelphia in 1787, tasked with revising the Articles of Confederation. The convention, attended by prominent delegates such as George Washington, James Madison, and Alexander Hamilton, ultimately drafted a new Constitution that would establish a stronger central government.
Key Beliefs and Arguments: Federalists Vs Anti Federalists Worksheet
Federalists, Federalists vs anti federalists worksheet
Federalists, led by Alexander Hamilton, advocated for a strong central government with the power to regulate commerce, tax, and raise an army. They argued that a centralized authority was necessary to maintain order, protect the nation from foreign threats, and promote economic prosperity.
Anti-Federalists
Anti-Federalists, led by Patrick Henry and George Mason, opposed the ratification of the Constitution. They feared that a powerful central government would infringe upon individual liberties and state sovereignty. They advocated for a weaker federal government with limited powers.
| Federalists | Anti-Federalists |
|---|---|
| Strong central government | Weak central government |
| Broad federal powers | Limited federal powers |
| Protection of individual liberties through a Bill of Rights | Protection of individual liberties through state constitutions |
The Federalist Papers and Anti-Federalist Writings
The Federalist Papers, a series of 85 essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay under the pseudonym “Publius,” were published in support of the ratification of the Constitution. These essays eloquently defended the principles of federalism and addressed the concerns of Anti-Federalists.
Anti-Federalists responded with their own writings, such as “The Federal Farmer” essays by Richard Henry Lee and “Cato’s Letters” by George Mason. These writings highlighted the potential dangers of a powerful central government and argued for the preservation of state sovereignty.
Ratification Process and the Bill of Rights
The ratification process of the Constitution was a contentious one, with both Federalists and Anti-Federalists actively campaigning for their respective positions. Ultimately, the Constitution was ratified in 1788, but only after the addition of a Bill of Rights, which addressed many of the concerns raised by Anti-Federalists.
- The Bill of Rights includes the first ten amendments to the Constitution.
- These amendments protect individual liberties, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to bear arms.
Legacy and Impact
The Federalist vs Anti-Federalist debate has had a profound impact on American politics and governance. The principles debated during this period continue to shape contemporary political discourse and constitutional interpretations.
Federalist ideas of a strong central government and broad federal powers have influenced the growth of the federal government and its role in American society.
Anti-Federalist concerns about individual liberties and state sovereignty have led to the development of a strong tradition of states’ rights and constitutional protections for individual freedoms.
Expert Answers
What were the key beliefs of the Federalists?
Federalists advocated for a strong central government, believing it could protect individual rights and promote economic prosperity.
What were the main concerns of the Anti-Federalists?
Anti-Federalists feared a powerful central government would erode state sovereignty and individual liberties.
How did the Federalist Papers contribute to the debate?
The Federalist Papers, written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay, provided influential arguments in favor of ratification.
What was the significance of the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights, added to the Constitution after ratification, addressed Anti-Federalist concerns by guaranteeing fundamental individual freedoms.