Student exploration uniform circular motion offers a captivating gateway into the world of physics, where the interplay between velocity, acceleration, and centripetal forces unfolds. This journey unveils the fundamental principles that govern objects moving in circular paths, providing a deeper understanding of everyday phenomena and technological advancements.
From celestial bodies orbiting the sun to amusement park rides spinning at dizzying speeds, uniform circular motion permeates our lives. This exploration empowers students to unravel the mysteries of these motions, fostering a profound appreciation for the intricate workings of our universe.
Uniform Circular Motion: Student Exploration Uniform Circular Motion

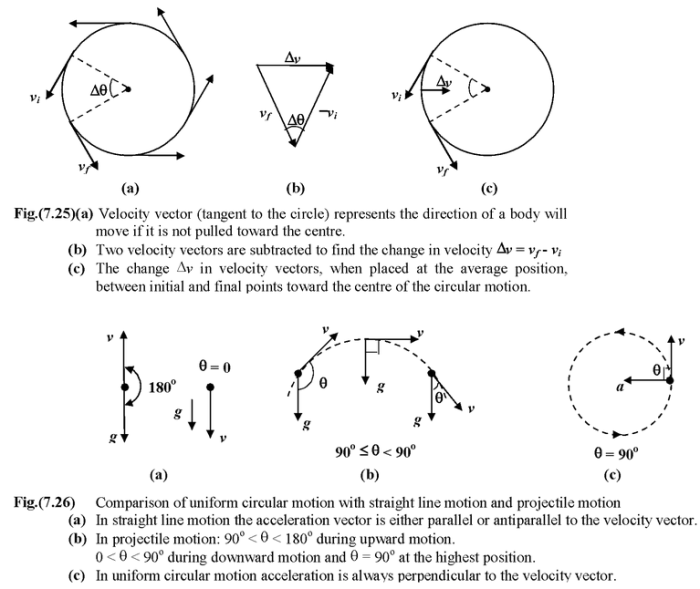
Uniform circular motion is a type of motion in which an object moves in a circular path at a constant speed. The object’s velocity is constantly changing direction, but its speed remains the same.
Examples of objects in uniform circular motion include:
- A car going around a curve
- A ball on a string
- A satellite orbiting the Earth
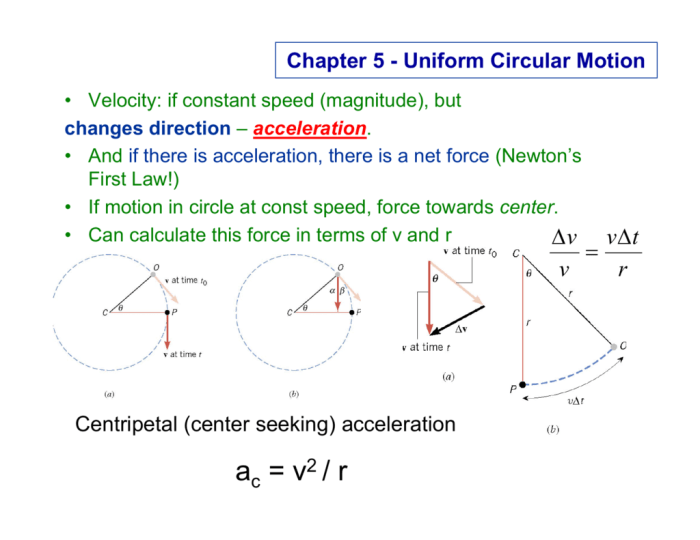
The relationship between velocity and acceleration in uniform circular motion is given by the following equation:
a = v^2/r
where:
- a is the acceleration
- v is the velocity
- r is the radius of the circle
Centripetal Force
Centripetal force is the force that keeps an object moving in a circle. It is always directed towards the center of the circle.
Examples of centripetal forces include:
- The force of gravity between the Earth and a satellite
- The tension in a string that is attached to a ball
- The friction between a car’s tires and the road
Applications of Uniform Circular Motion, Student exploration uniform circular motion
Uniform circular motion has many applications in everyday life, engineering and technology, and sports and recreation.
- Everyday life:Washing machines, CD players, and ceiling fans all use uniform circular motion.
- Engineering and technology:Centrifuges, turbines, and gears all use uniform circular motion.
- Sports and recreation:Roller coasters, merry-go-rounds, and bicycles all use uniform circular motion.
Experiments and Demonstrations
There are many ways to demonstrate uniform circular motion. One simple experiment is to tie a ball to a string and swing it in a circle.
Another way to demonstrate uniform circular motion is to use a centrifuge. A centrifuge is a machine that spins objects at high speeds. The centripetal force generated by the centrifuge keeps the objects from flying off.
Mathematical Analysis
Uniform circular motion can be described by the following equations:
v = 2πr/T
a = v^2/r
where:
- v is the velocity
- r is the radius of the circle
- T is the period of the motion
- a is the acceleration
Historical Perspective
The concept of uniform circular motion was first developed by the ancient Greeks. Aristotle believed that the planets moved in perfect circles around the Earth. This idea was later challenged by Copernicus, who proposed that the planets moved in circles around the Sun.
The laws of uniform circular motion were first developed by Galileo Galilei in the 17th century. Galileo showed that the acceleration of an object in uniform circular motion is proportional to the square of its velocity and inversely proportional to the radius of the circle.
General Inquiries
What is the key concept behind uniform circular motion?
Uniform circular motion occurs when an object moves in a circular path with constant speed, resulting in a constant change in direction and acceleration towards the center of the circle.
How does centripetal force affect objects in uniform circular motion?
Centripetal force is the inward force that keeps an object moving in a circular path, preventing it from moving in a straight line. It is directed towards the center of the circle and is provided by external forces such as tension, gravity, or friction.
Can you provide an example of uniform circular motion in everyday life?
A common example of uniform circular motion is a car going around a curve at a constant speed. The centripetal force in this case is provided by the friction between the tires and the road.