In the accompanying diagram demand is relatively elastic – In the accompanying diagram, demand is relatively elastic, indicating a strong responsiveness to price changes. This elasticity has significant implications for businesses, influencing revenue, profit margins, and strategic decision-making.
Elastic demand arises when consumers have readily available substitutes or the product is considered non-essential. Understanding the factors that affect elasticity enables businesses to adjust their pricing and marketing strategies accordingly.
Economic Factors Influencing Elasticity of Demand
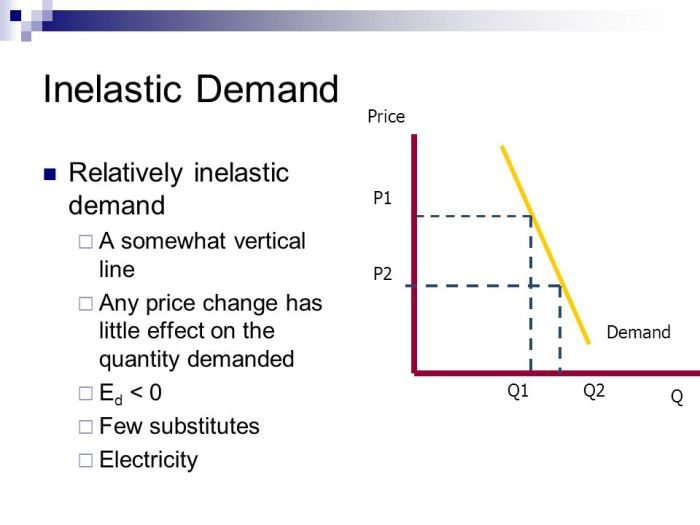
The elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price. In elastic markets, a small change in price leads to a significant change in quantity demanded. This is because consumers have many substitutes for the product or the product is not a necessity.
Factors that can affect the elasticity of demand include:
- Availability of substitutes:If there are many substitutes available, consumers are more likely to switch to a different product if the price of the original product increases. This makes demand more elastic.
- Necessity of the product:If the product is a necessity, consumers are less likely to reduce their consumption even if the price increases. This makes demand less elastic.
Graphical Representation of Elastic Demand
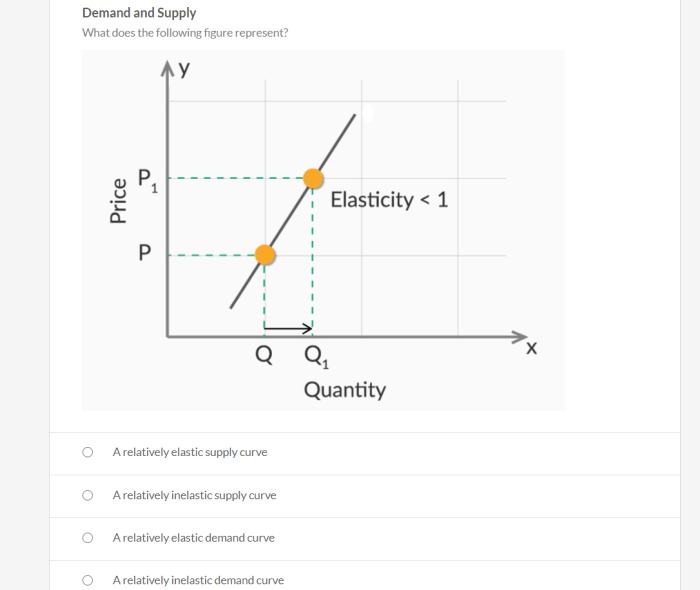
| Price | Quantity Demanded | Elasticity Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 100 | -2 |
| 12 | 80 | -2 |
| 14 | 60 | -2 |
The table shows an elastic demand curve. The elasticity coefficient is -2, which means that a 1% increase in price leads to a 2% decrease in quantity demanded. The demand curve is downward-sloping, which means that as the price of the product increases, the quantity demanded decreases.
Elastic demand curves differ from inelastic demand curves in that they have a steeper slope. This is because consumers are more responsive to price changes in elastic markets.
Implications of Elastic Demand for Businesses
Elastic demand has several implications for businesses:
- Revenue:If demand is elastic, a price increase will lead to a decrease in revenue. This is because the decrease in quantity demanded will outweigh the increase in price.
- Profit margins:If demand is elastic, a price increase will lead to a decrease in profit margins. This is because the decrease in revenue will be greater than the decrease in costs.
Businesses can implement several strategies to manage demand elasticity, such as:
- Product differentiation:By differentiating their product from competitors, businesses can make it less likely that consumers will switch to a different product if the price increases.
- Price discrimination:By charging different prices to different groups of consumers, businesses can capture more of the consumer surplus and increase their profits.
Examples of Elastic and Inelastic Demand
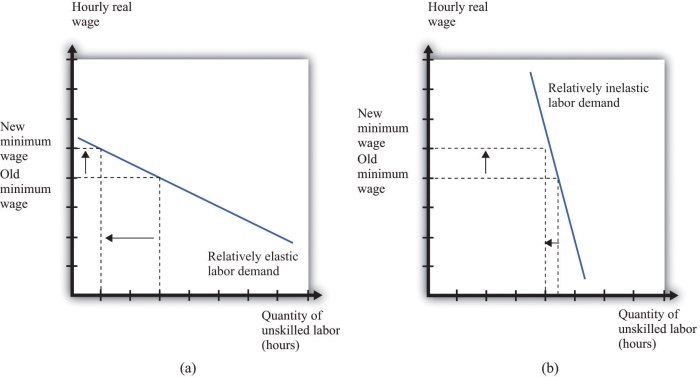
Some examples of products or services with elastic demand include:
- Luxury goods
- Entertainment
- Travel
Some examples of products or services with inelastic demand include:
- Gasoline
- Prescription drugs
- Electricity
The factors that contribute to the different elasticities of these products include the availability of substitutes and the necessity of the product.
FAQ Insights: In The Accompanying Diagram Demand Is Relatively Elastic
What factors can affect the elasticity of demand?
Availability of substitutes, necessity of the product, and consumer income levels.
How does elastic demand impact revenue?
Elastic demand can lead to significant revenue fluctuations in response to price changes.
What strategies can businesses use to manage demand elasticity?
Product differentiation, price discrimination, and loyalty programs.