Select the most accurate statement describing DNA replication complexes: These intricate molecular machines are the gatekeepers of genetic inheritance, ensuring the faithful duplication of DNA during cell division. Their precise choreography underpins the continuity of life, making them central to our understanding of biology and medicine.
DNA replication complexes are diverse in their composition and function, reflecting the complexity of the replication process. They orchestrate the unwinding of the double helix, the synthesis of new DNA strands, and the proofreading of errors, ensuring the integrity of our genetic blueprint.
DNA Replication Complexes
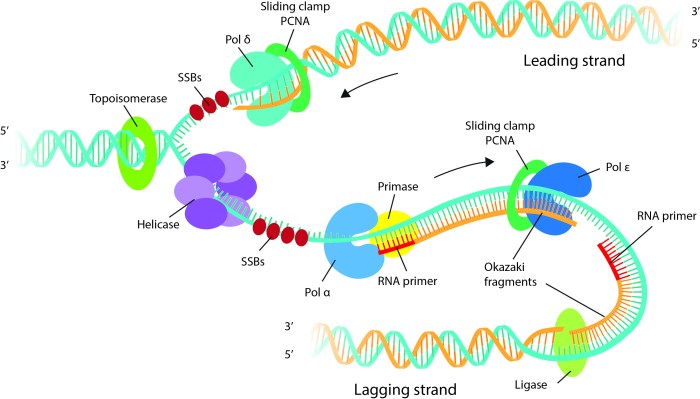
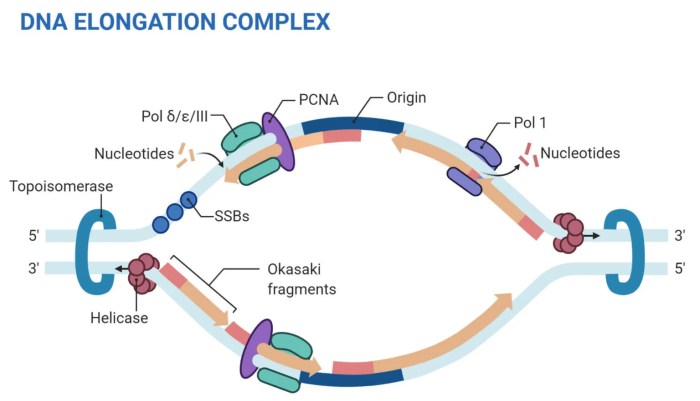
DNA replication complexes are large, multi-enzyme assemblies that carry out the complex process of DNA replication. They are responsible for copying the genetic material of a cell with high accuracy and efficiency, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information during cell division.DNA
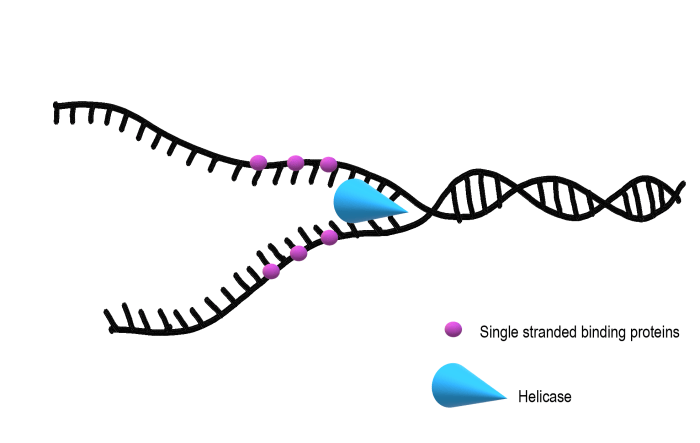
replication complexes are composed of numerous proteins, including DNA polymerases, helicases, primases, and single-strand binding proteins. These proteins work together to unwind the DNA double helix, synthesize new DNA strands complementary to the template strands, and proofread the newly synthesized DNA to ensure its accuracy.
FAQ: Select The Most Accurate Statement Describing Dna Replication Complexes
What are the key components of DNA replication complexes?
DNA replication complexes comprise a diverse array of proteins, including DNA polymerases, helicases, primases, and single-stranded DNA-binding proteins. Each component plays a specific role in unwinding the DNA helix, synthesizing new strands, and ensuring the fidelity of the replication process.
How are DNA replication complexes regulated?
DNA replication complexes are subject to intricate regulatory mechanisms that ensure the timely and accurate duplication of DNA. These mechanisms involve checkpoints that monitor the availability of nucleotides, the integrity of the template DNA, and the progression of the replication fork.